耐鹽堿雅羅魚(yú)遺傳資源研究平臺(tái)致力于系統(tǒng)開(kāi)發(fā)雅羅魚(yú)資源,深入探討魚(yú)類耐鹽堿的生理與分子遺傳機(jī)制,培育耐鹽堿魚(yú)類新品種,為我國(guó)水產(chǎn)科技事業(yè)發(fā)展提供科學(xué)的信息資源和技術(shù)支撐。平臺(tái)搜集了分布于我國(guó)不同水域類型中具有代表性的雅羅魚(yú)野生種,其中包括生長(zhǎng)在哈爾濱松花江和內(nèi)蒙古達(dá)里諾爾湖的瓦氏雅羅魚(yú)(Leuciscus waleckii)、由日本海溯河至綏芬河產(chǎn)卵的灘頭雅羅魚(yú)(L. brandti)、生長(zhǎng)在新疆額爾齊斯河的貝加爾雅羅魚(yú)(L. leuciscus baicalensis)和高體雅羅魚(yú)(L.idus)。雅羅魚(yú)具有耐高鹽堿、耐低溫及種間表型差異大等特點(diǎn),是開(kāi)展耐鹽堿魚(yú)類良種開(kāi)發(fā)和魚(yú)類耐鹽堿遺傳機(jī)制研究的模式實(shí)驗(yàn)材料。
目前我們利用這些資源已經(jīng)或即將開(kāi)展下列研究:
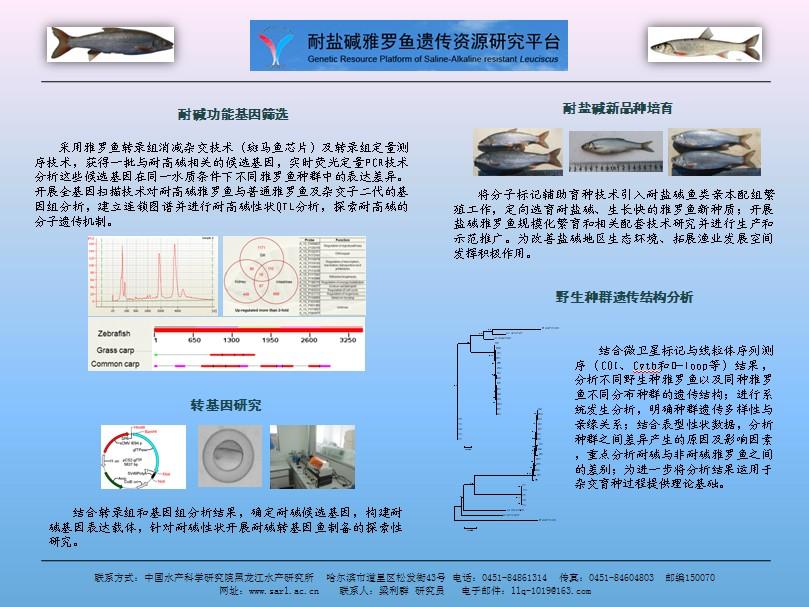
1) DNA分子標(biāo)記開(kāi)發(fā):將基因組克隆和轉(zhuǎn)錄組測(cè)序相結(jié)合,開(kāi)發(fā)雅羅魚(yú)SSR標(biāo)記、EST標(biāo)記和SNP標(biāo)記;
2) 野生種(群)遺傳結(jié)構(gòu)分析:利用分子標(biāo)記對(duì)搜集獲得的不同雅羅魚(yú)野生種(群)進(jìn)行全基因組掃描,分別建立遺傳背景檔案;
3) 遺傳連鎖圖譜構(gòu)建及QTL分析:根據(jù)耐鹽堿特性及表型特征,以不同親本組合制備雜交F2,建立標(biāo)記與性狀的連鎖關(guān)系,開(kāi)展耐鹽堿、側(cè)線鱗、鱗片大小、體型等性狀的QTL分析;
4) 耐高堿分子遺傳機(jī)制研究:利用斑馬魚(yú)芯片和轉(zhuǎn)錄組測(cè)序技術(shù),分析淡水和堿水瓦式雅羅魚(yú)鰓、腎、腸3個(gè)組織的基因表達(dá)譜差異個(gè)組織的基因表達(dá)譜差異,獲得一批與耐高堿相關(guān)的候選基因。并結(jié)合基因組耐鹽堿QTL分析結(jié)果,對(duì)雅羅魚(yú)耐高堿的分子機(jī)制進(jìn)行闡述;
5) 培育耐鹽堿新品種:根據(jù)雅羅魚(yú)的耐鹽堿特性及表型特征,將分子標(biāo)記輔助育種與傳統(tǒng)育種技術(shù)相結(jié)合,確定不同親本配組制備雜交F1,并通過(guò)對(duì)雜交子代生產(chǎn)性能比較,篩選具有優(yōu)良性狀的雜交種;利用篩選獲得的耐堿候選基因,通過(guò)轉(zhuǎn)基因技術(shù)構(gòu)建耐鹽堿魚(yú)類新品種。
上述研究工作的開(kāi)展必將推進(jìn)我國(guó)雅羅魚(yú)種質(zhì)資源深度挖掘及保護(hù)利用的進(jìn)程,同時(shí)也將對(duì)魚(yú)類耐鹽堿分子機(jī)制的深入研究奠定良好的基礎(chǔ)。培育的耐鹽堿雅羅魚(yú)新品種對(duì)我國(guó)北方水產(chǎn)養(yǎng)殖結(jié)構(gòu)的調(diào)整及鹽堿水域水質(zhì)改良具有十分重要的經(jīng)濟(jì)價(jià)值和生態(tài)意義。
INTRODUCTION
The platform of genetic resources for saline-alkaline resistant (SAR) Leuciscus will mainly focus on the introduction of the resources of Leuciscus distributed in China, the mechanisms of saline-alkaline resistance clarified in physiological and molecular genetic level, ,and the new varieties of SAR fish species produced through intercross or transgenosis. The representative wild species of Leuciscus distributed in different types of water environment hasve been collected, including the Leuciscus waleckii grown in Songhua River in Harbin and Dalinoer Lake in innerInner Mongolia, the L. brandti migrated from Japan Sea to Suifen River, the L. leuciscus baicalensis and L.idus grown in Erqis River in Xinjiang. The Leuciscus would be a good experimental model for studying the genetic mechanism of saline-alkaline resistance and breeding new SAR fish varieties, due to its excellent performances in high saline-alkaline and low temperature tolerance and remarkable phenotypic differences between species.
Presently, the studies have been or would be carried out as follows:
1). DNA marker preparation The DNA markers of SSR, EST and SNP will be identified based on the genome cloning and transcriptome sequencing.
2). Genetic structure analysis of wild populations Genome-wide scan will be performed for Leuciscus collected from different wild populations by use of the molecular markers.
3). Genetic linkage map and QTL analysis Based on the characteristics of saline-alkaline resistance and phenotypic differences of the wild Leuciscus, the hybrids F2 will be produced to build the genetic linkage constructs and conduct QTL analysis, such as profiles of saline-alkaline resistance, number of lateral line scales, scale size, body shape and so on.
4). Molecular genetic mechanism of saline-alkaline resistance The gene expression profiles of gill, kidney and intestine of L. waleckii from freshwater and alkaline water will be obtained using zebrafish microarray and transcriptome sequencing techniques. A number of candidate genes associated with alkaline resistance will be identified. The mechanism of saline-alkaline resistance would be studied deeply combining the results of QTL fine mapping.
5). Breeding new varieties Based on the characteristics of saline-alkaline resistance and phenotypic features of the wild Leuciscus, the hybrids with superior characteristics will be propagated by combination of the molecular marker-assisted and conventional breeding techniques, and the new varieties of SAR fish species could be prepared by transgenic technology as well.
These researches mentioned above will not only promote the resources utilization and corresponding protection strategies making for Leuciscus, but also lay a good foundation for the studies of the molecular mechanisms of saline-alkaline resistance for fish species. The selected-bred new varieties are of important meanings economically and ecologically in adjusting the aquaculture structure and improving the quality of saline-alkaline water in northern China.
附課題組宣傳資料: